Building Apps That Grow With Your Business
Every ambitious business leader dreams of growth. You envision expanding your customer base, launching new product lines, and scaling your operations to new heights. However, this exciting journey can come to a sudden halt if your foundational technology cannot keep up. An application that works perfectly for a team of ten can easily fracture under the pressure of a thousand users, leading to crashes, data corruption, and a frustrated customer base.
The difference between an application that fuels growth and one that stifles it lies in a single, critical concept: scalability. Building a scalable application is not an accident; it is the result of deliberate architectural choices made from day one. It requires a strategic focus on a robust foundation, granular control over access, and the flexibility to adapt to future demands.
This article will explore the essential pillars of scalable software—architecture, roles and permissions, and extensibility—and demonstrate how a strategic approach ensures your applications are a catalyst for growth, not a barrier to it.
The Bedrock of Scalability: Robust Architecture
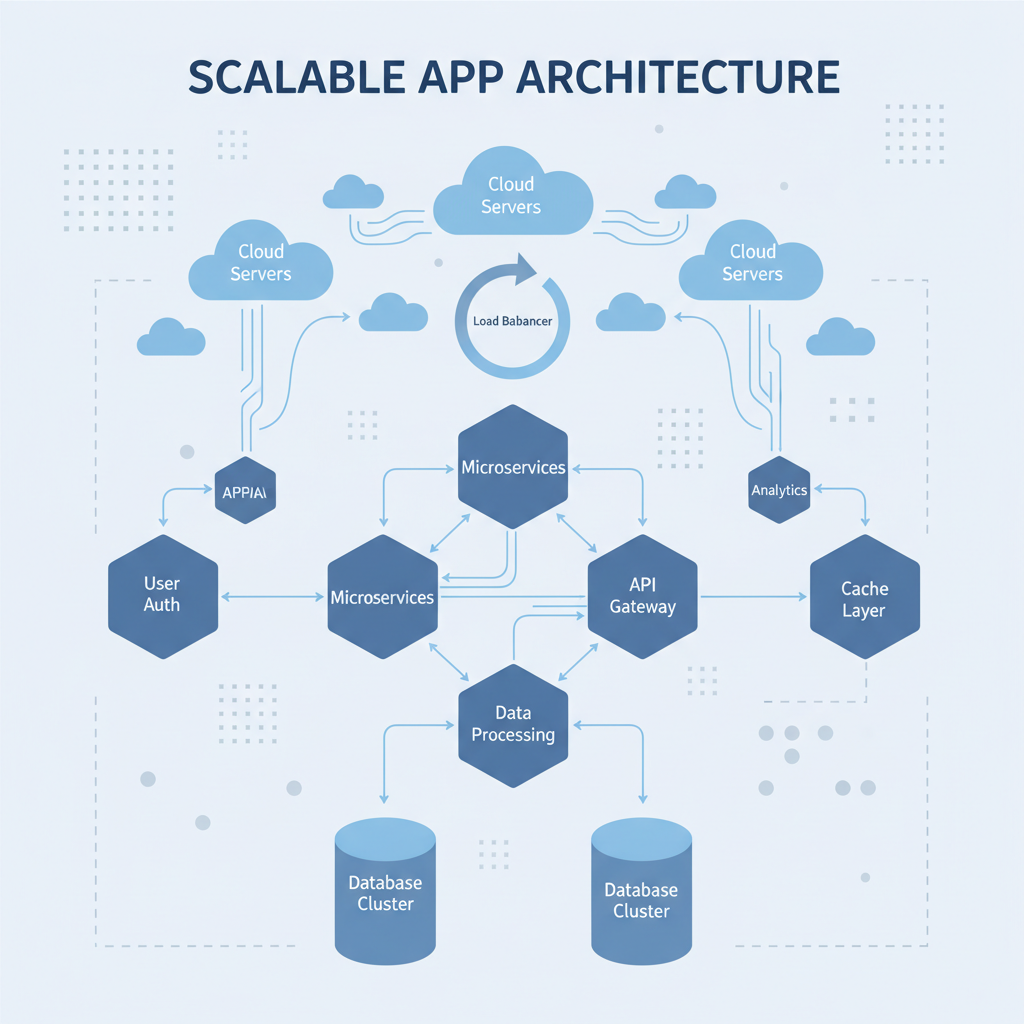
The architecture of your application is its blueprint. It dictates how components communicate, how data flows, and how the system responds to stress. A poorly designed architecture is like building a skyscraper on a weak foundation; it is destined to crumble under its own weight.
A scalable architecture is designed for growth. It anticipates increased user loads, larger datasets, and more complex workflows. Key characteristics include:
- Modular Design: Instead of a single, monolithic block of code, a modular architecture breaks the application into smaller, independent services or components. This means you can update or scale one part of the system (like payment processing) without impacting another (like user authentication). This separation is fundamental to maintaining stability and agility as you grow.
- Stateless Components: Scalable applications often treat interactions as stateless, meaning each request contains all the information needed to process it. This allows you to easily distribute user traffic across multiple servers, as no single server holds critical session data. This is essential for handling sudden spikes in activity without performance degradation.
- Efficient Database Management: As your user base grows, so does your data. A scalable architecture includes an optimized database schema, effective indexing, and caching strategies to ensure that data retrieval remains fast, even with millions of records.
Building this kind of architecture from scratch requires deep engineering expertise. This is precisely why low-code platforms that are built upon proven, modern frameworks are so valuable. For instance, RadSystems generates applications using powerful frameworks like PHP Laravel, ASP.NET Core, and Python. This provides you with an enterprise-grade architectural foundation out of the box, ensuring your application is built to scale from its very first line of code.
The Gatekeepers: Why Roles and Permissions Matter for Scale
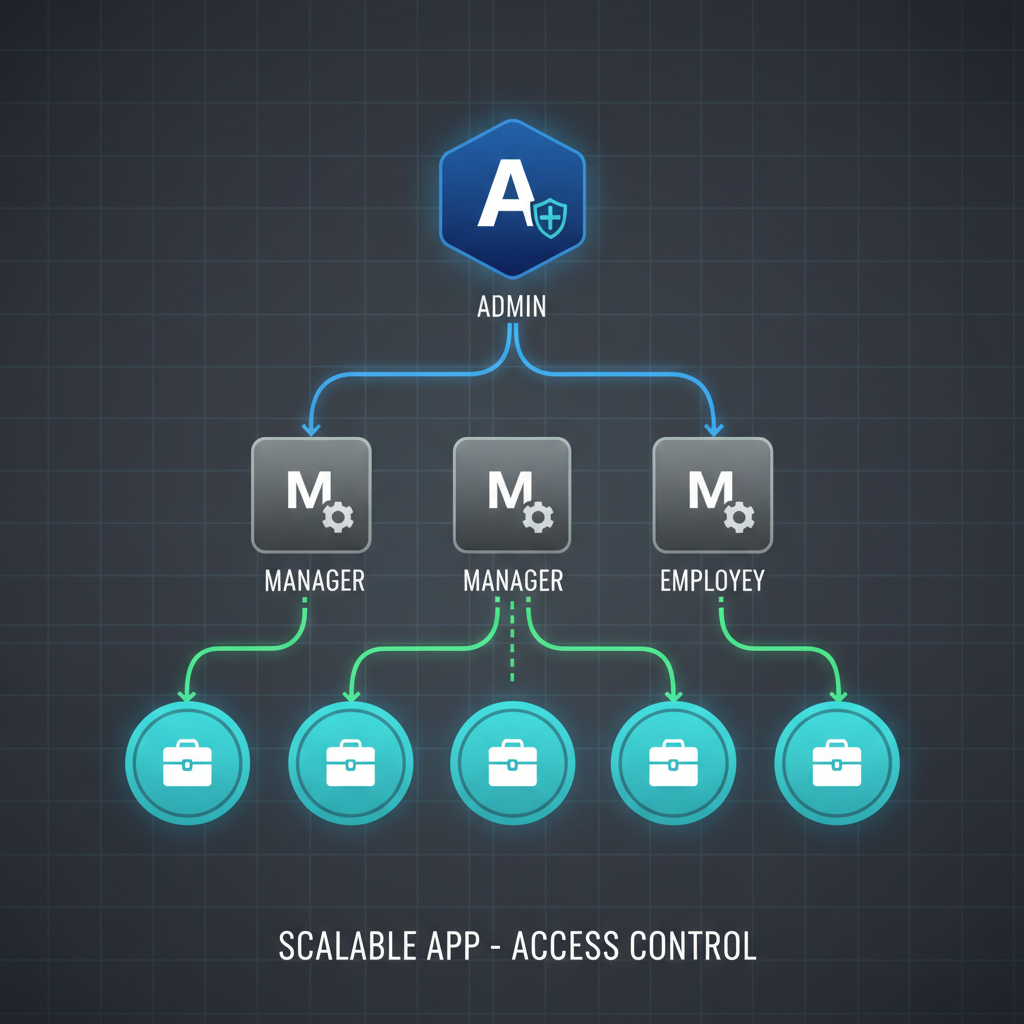
As your business expands, so does your team. You will have employees, managers, administrators, and potentially contractors, all needing different levels of access to the application. An application that cannot differentiate between these roles is a massive security risk and an operational bottleneck.
A scalable system must have a sophisticated system for managing roles and permissions. This involves:
- Granular Access Control: You must be able to define precisely what each user can see and do. A sales representative should not have access to financial reports, and a customer service agent should not be able to alter the application's core settings. This granularity prevents accidental data modification and protects sensitive information.
- Hierarchical Roles: Effective systems allow you to create roles with inherited permissions. For example, a "Manager" role might have all the permissions of an "Employee" role, plus the ability to approve requests. This simplifies administration and ensures consistency.
- Dynamic Assignment: As your organization evolves, you need the ability to easily assign and reassign roles without requiring developer intervention. This administrative flexibility is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency as teams change and grow.
Without a robust permissions model, every new hire becomes a security liability, and simple administrative tasks become complex chores. Platforms designed for enterprise use, like RadSystems, build this functionality into their core, allowing you to create and manage complex role-based access control (RBAC) systems visually.
The Future-Proofing Factor: Designing for Extensibility
Your business needs today are not your business needs tomorrow. You will adopt new tools, enter new markets, and develop new processes. An application that cannot adapt to these changes will quickly become obsolete. This is where extensibility comes in.
Extensibility is the quality of a system that allows for new functionality to be added with minimal effort and without modifying the core code. It ensures your application can evolve alongside your business. Key elements of extensibility include:
- API-First Design: An application built with an API-first approach exposes its functionality through well-documented endpoints. This allows you to easily integrate your application with other software, such as CRMs, accounting systems, or marketing automation platforms. This turns your application into a central hub, not an isolated silo.
- Clean and Accessible Codebase: While low-code platforms accelerate development, true extensibility requires that the generated code is clean, human-readable, and adheres to industry best practices. This allows professional developers to "look under the hood" and inject custom code, connect to specialized third-party libraries, or build entirely new modules when a unique business need arises.
- Plugin and Module Support: A truly extensible platform enables the creation of reusable plugins or modules. This means you can develop a custom feature once and deploy it across multiple applications or share it with other teams, compounding your development efficiency over time.
RadSystems champions this principle by generating standardized, readable code. This empowers developers to take the application 90% of the way with low-code speed and then add that final 10% of highly custom functionality without being constrained by a "black box" system.
Build for Tomorrow, Starting Today
Building a scalable application is a strategic imperative for any business with growth ambitions. It requires a disciplined focus on robust architecture, granular permissions, and forward-thinking extensibility. Neglecting these pillars may offer short-term speed but will inevitably lead to long-term pain, costing you time, money, and customer trust.
The modern development landscape offers a powerful solution. You no longer have to choose between the speed of low-code and the structural integrity required for scale. Platforms like RadSystems provide the best of both worlds, offering a rapid application development environment built on an enterprise-grade foundation.
Do not wait for your application to break before you think about scalability. Make the right architectural decisions from the start.
Ready to build applications that grow with your business? Explore how RadSystems provides the framework for building robust, scalable, and extensible enterprise solutions.

